MicMacRoom Tutorial: 02 Fontaine
Sommaire
Fontaine Tutorial
Description
In this tutorial, we go further into command details, process, results, products, etc. Here you will learn how to process a dataset of a circular point of view around an object. To achieve this, we are going to create a dense point cloud of a 3D object.
Download
You can find this dataset at [1](https://micmac.ensg.eu/data/fontaine_dataset.zip). Once you have downloaded it, you have to unzip the ".zip" archive.
Presentation
The folder contains 30 JPG files. In this dataset, there isn't any data about the camera which was used. The shooting set contains 30 images, all taken with the Canon 70D camera with an 18mm lens. The camera saves metadata for all the pictures (exif data). If you are looking in the property data of each picture, the 18mm lens is mentioned and the various chosen settings while the production of this dataset was realized (opening, break, ...). There are 5 parts in this dataset:
- 4 parts include 4 different points of view of the fountain. Each part was created with a cross points of view. This means there is one master image at the center and 4 images around it (top, bottom, left, and right from the master image).
- 1 part contains the other images (IMG.*JPG). These images are images link, this means that they will allow to link the 4 other parts together. They won't be used to generate the dense clouds points.
Tutorial
0 Project creation and Image Importation
First and foremost, open MicMacRoom and save your project, you can then use the File > Import Images to import the images from the dataset. Then select all of the nodes in the graph editor and delete them all.
1 Base Element
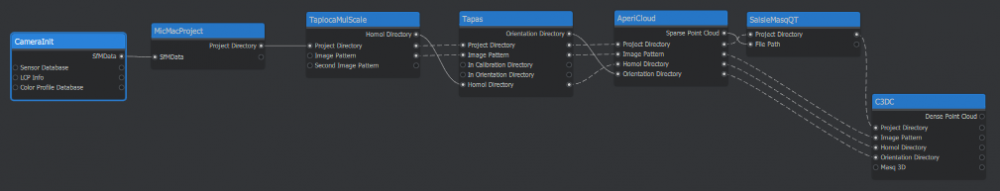
To allow MicMacRoom to work we need to specific nodes at the beginning of the pipeline. These are: CameraInit which will recover the image information from the camera and MicMacProject which will create the directory. To add a node, place your cursor in the graph editor, right-click and select the node you want, either by searching the list of by doing of search by keyword. CameraInit is placed first and MicMacProject second. You can then take the SfmData output of CameraInit (Output are located on the right of a node) and link it with the SfmData input of MicMacProject (Input are located on the left of a node), if you see a line between the two nodes, then you have succeeded. You can also check the MicMacProject node and left-click on it to see that the SfmData parameter now has an address. If you have created a wrong link, you can delete it by pressing right-click and remove on it.
2 Tie-points search
To perform the tie-points search, we use the TapiocaMulScale node (Important: In MicMac, Mulscale is a parameter of Tapioca however in MicMacRoom, there are different Tapioca modules for certain parameters, so it is important to choose TapiocaMulScale) Then link the project directory from MicMacProject to TapiocaMulScale and, in this node, set Image Size low to 500 and Image Size high to 2500. The MulScale pattern allows making a search for similar points firstly on sub-sampled images. On this dataset, it will be on 500pixels on the biggest side instead of 5472 on the originals images. This allows knowing which images have some tie points between them and to only run the tie-points search at a bigger resolution (here 2500) on the optimal sets of images.
3 Internal Orientation and Relative Orientation
We are looking now to know the position of the camera, in relative to each other, but also to know the calibration of the camera used. For this, we use the Tapas node. As usual, first, we must link the different modules. From TapiocaMulScale, link the Homol Directory, Project Directory, and Image pattern to Tapas. Then in Tapas, set Calibration Model to RadialStd (RadialStd is the pattern generally used for classic cameras).
4 Visualize Relative Orientation
The AperiCloud command allows generating a 3D clouds points, containing all the tie-points obtained with TapiocaMulScale, and the position of the camera used as a Tapas input. Create an AperiCloud node and link Project directory, Image Pattern, Homol Directory, and Orientation Directory from Tapas. The result of this command can be seen, for example, with the Meshlab software (Visualization in Meshroom is not available at the moment due to differences between the MicMac output format: .ply and the Meshroom preferred format: .abc). So we can see that the 4 parts containing 5 images around the fountain are connected between them thanks to the images link.
5 Masq creation
We will now draw a 3D mask, from the AperiCloud_Fontaine.ply file. Create a SaisieMasqQT and link the project directory. Then, link Sparse Point Cloud from AperiCloud into File Path of SaisieMasqQT. This node will open a new window where we will be able to draw the mask on the point cloud. The resulting file will have a name like AperiCloud_Fontaine_polygo3d.xml. (The name of this file depends on the output name parameter of the Tapas) Be aware that since the SaisieMasqQT node technically doesn’t output anything, Meshroom will not wait for you to draw the mask to start the next node. This will lead to an incorrect result, but we will be able to fix this issue later.
6 Densification
We can now run the 3D reconstruction with the C3DC command. First, create a C3DC node. Connect the project Directory from either AperiCloud or SaisieMasqQT. You must also link Image Pattern, Homol Directory, and Orientation Directory from AperiCloud. Then, set the C3DC mode to BigMac and in the Masq 3D parameter, put the full name of your masq file (something like: AperiCloud_Fontaine_polygo3d.xml).
This is the expected Pipeline after following this tutorial:
Running the pipeline
- Press start
- Once the program reaches the SaisieMasqQT, create and save your masq in the new window.
- Press stop
- Right-click on C3DC then delete data.
- Check if the C3DC parameters are still correct (especially the Masq 3D)
- Then press start again
- Once the C3DC node becomes green, you can check the results.